Enterprise Architect
Addressing Data Privacy Through an Intelligent Data Fabric
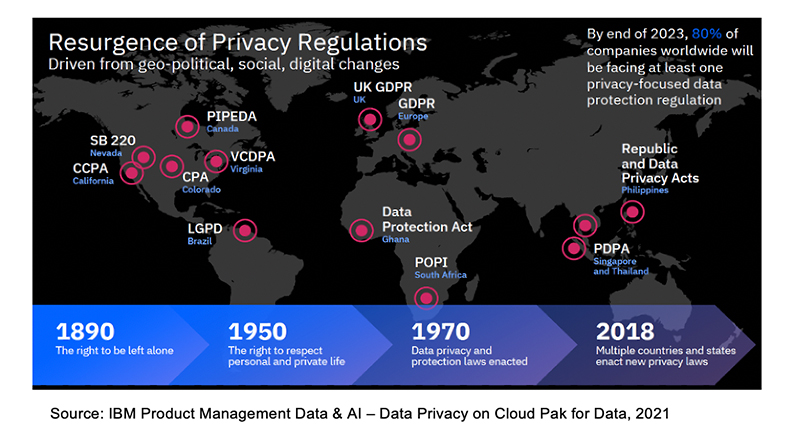
One of the cornerstones of a robust data fabric architecture is an automated and centralized data governance capability that ensures compliance of data privacy regulations. The ability to enforce data governance has become paramount with the introduction of many new data privacy regulations such as U.S. based regulations CCPA (California Consumer Protection Act), SB 220 in Nevada, CPA (Colorado Privacy Act), and VCDPA (Virginia Consumer Data Privacy Act). Many of these data privacy regulations are designed to protect PII (Personal Identifiable Information) data. The explosion of PII data volumes has further burdened IT organizations to ensure compliance with these data privacy regulations while maintaining necessary access to sensitive data within an organization.
Creating a single enforcement mechanism that is data policy-driven ensures appropriate, timely access to sensitive data. Instead of data “gate keepers” bearing the burden of controlling access to private information, an intelligent data fabric architecture provides for free flow of information in a controlled manner. This architecture enables data stewards to provide the necessary “shepherding” of sensitive data brought into the organization. Data stewards define and develop data access policies which provide a single point of enforcement over private information while allowing legitimate data access to support self-service reporting and analytics.
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST)’s Guide to Protecting the Confidentiality of PII (Personally Identifiable Information) defines “personally identifiable” as information like name, mother’s maiden name, social security number, passport number, Tax ID number, address, email address, cell phone number, vehicle registration numbers, private health Information (PHI) like date of birth, weight, health records, race, gender and biometric records. Any of these or combination of these can be used to distinguish or trace an individual’s identity are considered PII.
IBM Cloud Pak for Data – Intelligent data fabric architecture
IBM’s Cloud Pak for Data Intelligent data fabric architecture provides policy-driven data governance automation that addresses ongoing concerns around data privacy and PII data. Watson Knowledge Catalog AI-imbedded data management capabilities provide for the cataloging and governing of sensitive data types across hybrid data architecture landscapes.
These include:
- AutoCatalog – which provides data discovery and assignment of sensitive business terms, auto profiling of data assets, automated data classification of PII (Personal Identifiable Information). Intelligent AI-imbedded technologies can recognize data patterns of PII data assets thereby improving the ability to identify each occurrence of sensitive data across many data platforms. Automating the discovering of PII data assets through AI-based data recognition patterns helps to maintain a dynamic data catalog across a diverse data landscape. IBM Cloud Pak for Data auto discovery utilizes Watson’s AI-based data recognition to provide quick and comprehensive identification PII data assets that can be automatically published to a data catalog (collectively referred to as AutoCatalog).
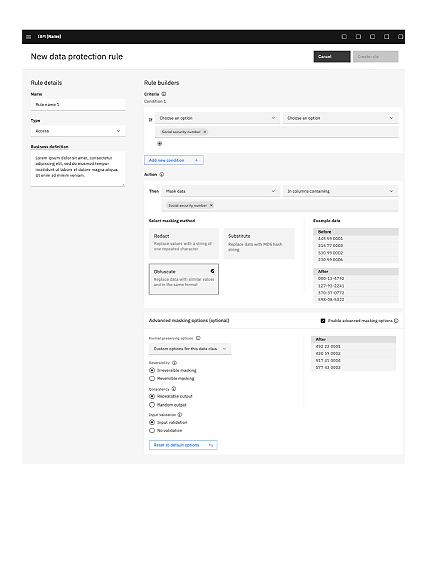
- AutoPrivacy – IBM Cloud Pak for Data’s Integrated Data Policy and Data Protection Rules combined with dynamic data masking and user access control provide the toolset to bring the data fabric architecture for data privacy to life (referred to as AutoPrivacy).
AutoPrivacy: Employs AI to intelligently automate the identification, monitoring and, subsequently, the enforcement of policies on sensitive data across the organization. AutoPrivacy is a key aspect of the universal data privacy framework available within IBM Cloud Pak for Data. Spanning the entire data and AI lifecycle, this framework allows business leaders to provide the self-service access data consumers need without sacrificing security or compliance. Build a better strategy for governance risk and compliance by eliminating compliance “blindspots” and minimizing risk.1
The goal of auto privacy is to streamline and automate the identification tagging and masking of private information to limit access and visibility to only users with a “need to know basis”. This is accomplished through the creation and implementation of both data policies and data protection rules. Data polices represent the stated company goal as it relates to data protection. For example, a data policy would be defined as “Protect Customer Data”. Data protection rules execute against information assets to screen or mask the data.
Use Case – Regulatory Compliance and Data Modernization
Mainline is working with a North America regional bank in adopting IBM Cloud Pak for Data to address regulatory compliance needs and enterprise data modernization requirements as part of their digital transformation. The architecture provides the Bank the ability to meet Dodd Frank and Current Expected Credit Loss (CECL) regulatory compliance requirements and at the same time has allowed significant value to be captured from the initiative. Discovery of sensitive data is now architected and automated within Cloud Pak for Data, which provides necessary “data masking” for regulatory audits. Mainline and IBM’s solution has increased data security while also meeting regulatory needs and it is supporting new business processes paramount for their growth strategy.
Summary
The demands of data privacy regulations are met through automated data governance in a data fabric architecture. Continual monitoring through data quality analysis will ensure compliance. Next in this series on IBM Cloud Pak for Data‘s Watson Knowledge Catalog, we will take a closer look at IBM Open Pages and how it is enabling a full 360 view of identifying, managing and monitoring a wider range of risk and regulatory compliance challenges.
More Information
Mainline offers a comprehensive portfolio of data management, governance, data integration, business analytics, AI, and ML solutions. For more information, contact your Mainline Account Executive directly or click here to contact us with any questions.
1 Source: Intelligently Automate Data and AI with the Next Generation of IBM Cloud Pak for Data | IBM
You may be interested in:
BLOG: Red Hat OpenShift on LinuxONE and IBM Z running under KVM
WEBINAR ON-DEMAND: Cloud Pak for Data – Turning Data into Insights (54:32)
VIDEO: Cloud Pak for Data – Make your Data Ready for AI & Cloud (2:09)

